Early Warning Signs of Hearing Loss You Might Be Missing
Most people don’t wake up one day and suddenly can’t hear.

Most people don’t wake up one day and suddenly can’t hear.

Visiting a hearing care professional is not just about testing your
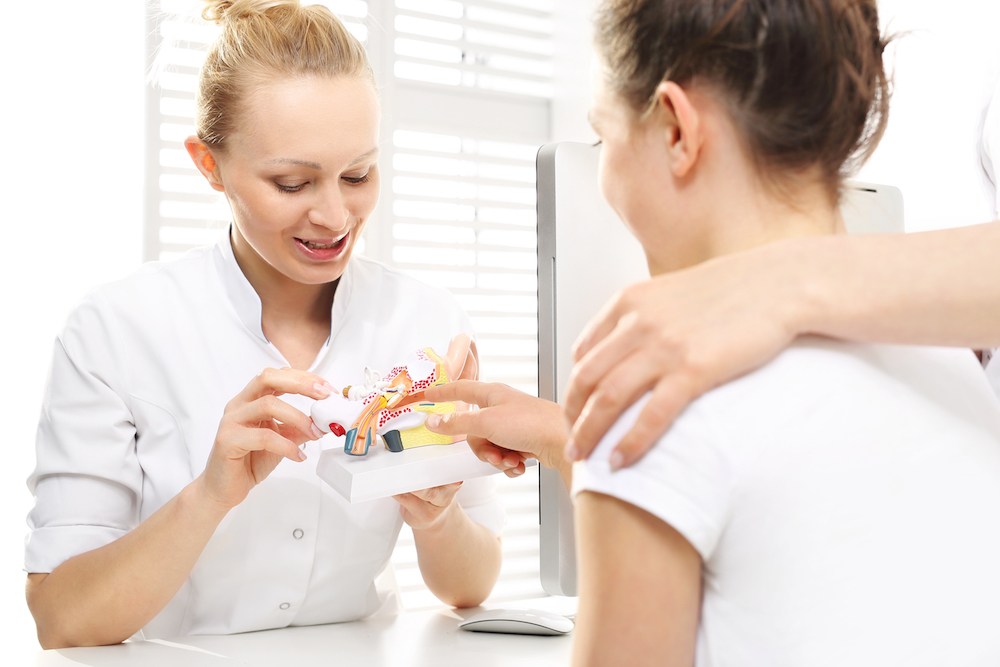

Virtual reality (VR) technology is beginning to influence the way hearing